提出 REAL
Related Work
传统 closed-set LIDAR语义分割
point-based methods: point-net / point-net++ 但是有性能限制
voxel-based methods: Cylinder3D,三维数据集SOTA,本文的base architecture
open-set 但是2D:
uncertainty-based methods:
generative model-based methods:
Stochastic Gradient Langevin Dynamics (SGLD)
Open-world
Methodology
REAL: Redundancy Classifier Framework
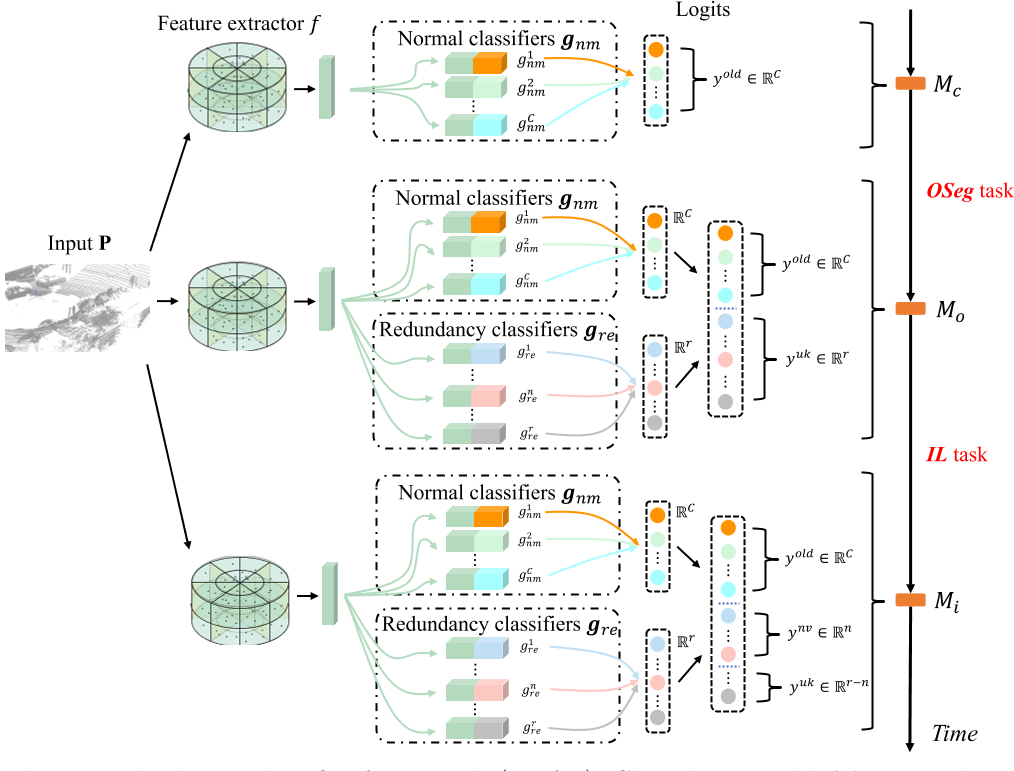
Oseg: Open-set Semantic Segmentation
将模型从$\mathcal{M}_c$训练到$\mathcal{M}_o$ ,提出两个训练策略:Unknown Object Synthesis,Predictive Distribution Calibration
- Unknown Object Synthesis
- Predictive Distribution Calibration
deep metric learning
open-world 和 open-set 有何不同
不必太关注open-world 与 open-set 差异,但可以多留意生成式模型的后续研究
为什么uncertainty-based methods: the network predicts the novel classes as old classes with high confidence scores
“cGAN只能重建通道信息而保持几何信息不变”是什么意思,为什么这种特性就不适用点云语义分割
与该项目无直接联系,后续可以专门研究生成式的模型
Cylinder3D文章中写到:由于室内采用的传统分割方法(PointNet…)的性能依赖于点云分布的均匀性和密度不变性,不能直接迁移到室外点云分割;实际面对室内场景分割,传统方法和Cylinder3D方法哪个更好?原因是什么?(室内种类多 / 点云均匀性与密度)
Problem: Open-World problem, comprising Oseg open-set semantic segmantation & IL incremental learning
Framework: REAL Redundancy Classifier Framework -> provide dynamic architecture
Training strategy: 1. unknown object synthesis 2. predictive distribution calibration 3. pseudo label generation
Dataset: SemanticKITTI & nuScenes